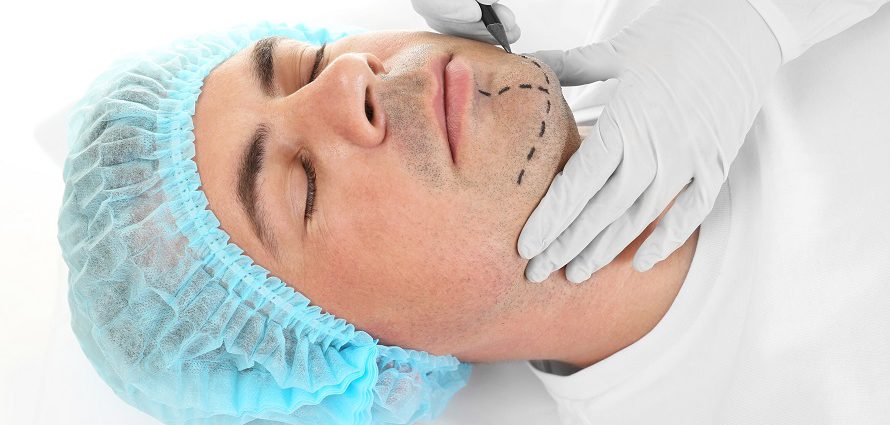
Chin Surgery: Augmentation (Genioplasty) and Reduction (Mentoplasty)
Here you’ll find information on:
- Options and combinations
- Getting started
- Mentoplasty: chin reduction
- Genioplasty: chin augmentation
- After surgery
- Complications and risks
- Consult a qualified plastic surgeon
- Costs
A balanced facial appearance depends partly on the shape and size of your chin in relationship to your nose. Chin surgery can reduce (mentoplasty) or augment (genioplasty) the chin to give your face a more balanced appearance.
A recent study of facial bones by the American Society of Plastic Surgeonsdemonstrated that individual facial bones shift, reduce, or enlarge with age. Because of the age-related nature of the changes, most chin surgery patients are adults.
Options and Combinations

Other procedures may be performed with chin surgery. For example, liposuction may be used to treat a double chin or to remove excessive fat in the chin area and neckline. Your surgeon may suggest chin surgery as a supplement to nose reshaping, because a small chin can make the nose appear larger. Chin surgery may be recommended as part of a combination treatment plan for a facelift or buccal fat extraction patient as well.
For a droopy chin (sometimes call “witch’s chin”), your doctor may recommend corrective elevation. Orthognathic chin surgery is another option, which treats birth defects causing dental malocclusion, which inhibits the ability to eat.
Getting Started with Chin Surgery
Chin surgery is usually performed in an outpatient surgical center or hospital. The procedure may be performed under local anesthesia (sedated, numbed, and awake). For more complicated cases, general anesthesia may be used (asleep). Patients usually return home within hours of the procedure. Some patients require an overnight stay. Depending upon the extent of the case, time in surgery may be one or more hours.
To decide how to proceed, the surgeon will examine your chin and jaw, and weigh factors that could influence the outcome of surgery, such as your age, skin type, and whether you are psychologically prepared for treatment.
Mentoplasty: Chin Reduction
During mentoplasty surgery, the surgeon makes an incision in one of two possible locations:
- under the lower lip inside the mouth
- under the chin in an inconspicuous location
The surgeon will then use an electrical instrument (a bone burr or a drill) to reduce and reshape the bone to create a more natural appearance. The surgeon will stitch the incision closed and apply tape to the chin area.
Genioplasty: Chin Augmentation
Genioplasty can be performed by the use of a chin implant to augment a receding chin, or by the surgical advancement of the bone itself. Once you and your surgeon decide whether to use a silastic chin implant or to advance your own bone, the incision will be chosen.
If you choose a chin implant, the incision is in one of two possible locations:
- under the lower lip inside the mouth
- under the chin in an inconspicuous location
The implant is placed in an appropriately sized pocket. Sizers are used to achieve the best appearance; then the actual implant is carefully placed and the incisions are closed.
If you choose to advance bone in the chin, the surgeon makes an incision under the lower lip inside the mouth using a powered saw with a special blade to separate the edge of the chin bone. The surgeon moves the separated chin-bone tip forward and positions it with wires or special bone plates and screws. Finally, the surgeon stitches the incision closed and applies tape to the chin area.
After Chin Surgery
You may also experience significant swelling or discoloration in the treated area, which will subside over the course of several weeks. The stitches are typically removed within seven days of the procedure.
Follow your doctor’s postoperative instruction list to help reduce the risk of complications. There may be some pain, which can be managed with oral medications. The surgeon may have recommendations to reduce swelling, such as elevating your head. Normal activities can be resumed typically within seven days.
Complications and Risks of Chin Surgery
Any plastic surgery procedure poses risks. Complications in the mentoplasty or genioplasty procedures do not occur often. Although rare, some patients may develop an infection in the chin or lip area, usually treated with antibiotics. The surgeon may recommend a waiting period to see if the infection resolves itself with antibiotic treatment. In rare instances an infection requires surgical drainage. Scar tissue formation is also a possibility. Over time, portions of the bone may erode; however, this does not typically cause any medical concerns, discomfort, or changes in the appearance of the chin.
In the genioplasty procedure, wires or plates are removed if they cause discomfort. Patients may experience lack of sensitivity in the chin or lip area; however, the numbness is usually temporary. In rare cases, sensitivity loss may be permanent. It is important to note that complications are infrequent and options are available to treat complications.
Consult a Qualified Plastic Surgeon
Consulting a qualified plastic surgeon will enable you to choose the best treatment plan for your condition and your goals. During your cosmetic surgery consultation, the surgeon will complete a medical evaluation and will describe the technique, the type of anesthesia to be used, the surgical facility, any additional surgery, risks, and costs.
It’s important to choose a board-certified plastic surgeon from the American Board of Plastic Surgery with extensive experience in mentoplasty, genioplasty, and all of the chin-related procedures. Board certification may not always guarantee the best results; however, board certification does require specific and rigorous surgical education and training that improves the odds for a successful outcome.
The type of certification is also important. There are more than 150 self-designated boards, but only a handful that are designated by the American Board of Medical Specialties (ABMS), such as the American Board of Plastic Surgery. A select number of surgeons focus in the area of plastic reconstructive surgery to better serve the needs of chin-surgery patients with deformities.
Here are some tips to consider when consulting a plastic surgeon:
- Review the surgeon’s credentials, education, training, type of board certification held, and the number of times that the treatment has been performed by the plastic surgeon.
- View before-and-after photos of the surgeon’s patients who received chin surgery to help set reasonable expectations.
- Bring a photo of the results you would like the see. The surgeon can help determine if this is a reasonable expectation.
- Inquire about the type of equipment used, where the procedure will be performed, and extent of the treatment plan.
- Inquire about the specific technique that is recommended for your situation. Techniques may vary among surgeons and patients.
- Review the preoperative and postoperative instruction list provided by the surgeon. These instructions may include:
1) no eating or drinking after midnight before surgery
2) a prescribed antibiotic for both before and after the procedure
3) ceasing certain medications
4) having someone drive you home after the procedure
5) having someone help with daily activities for at least 24 hours
6) diet restrictions (liquid or soft foods) for about a week after surgery
Chin Surgery Costs
Chin surgery costs consist of three fees: the anesthesia fee, the hospital or facility fee, and the surgeon’s fee. Costs vary depending on the complexity of the procedure. For example, more complicated surgery may take several hours: this factor increases surgical, anesthesia, and facility time, significantly affecting the total cost of the procedure.
If general anesthesia is administered and an overnight hospital stay is required, the costs will be greater than if local anesthesia is used, without a hospital stay. The facility where the surgical procedure is performed impacts cost as well. A comprehensive treatment plan may include more than one procedure. If multiple procedures can be performed at the same time, then certain fees may be combined.
Average fees for the mentoplasty or genioplasty procedures can range from $3,000 to $10,000. These costs vary based on the extent of the procedure, expertise of the surgeon, and the length of recovery.
Benefits vary among insurance carriers. Insurance may pay all or a portion of the procedure if the procedure is deemed medically necessary as the result of a birth defect or traumatic injury. Consult your surgeon about whether your insurance carrier will be responsible for the medical bills.
Payment
If the cost of the procedure is too large for you to pay at once, ask your surgeon about payment plan options.